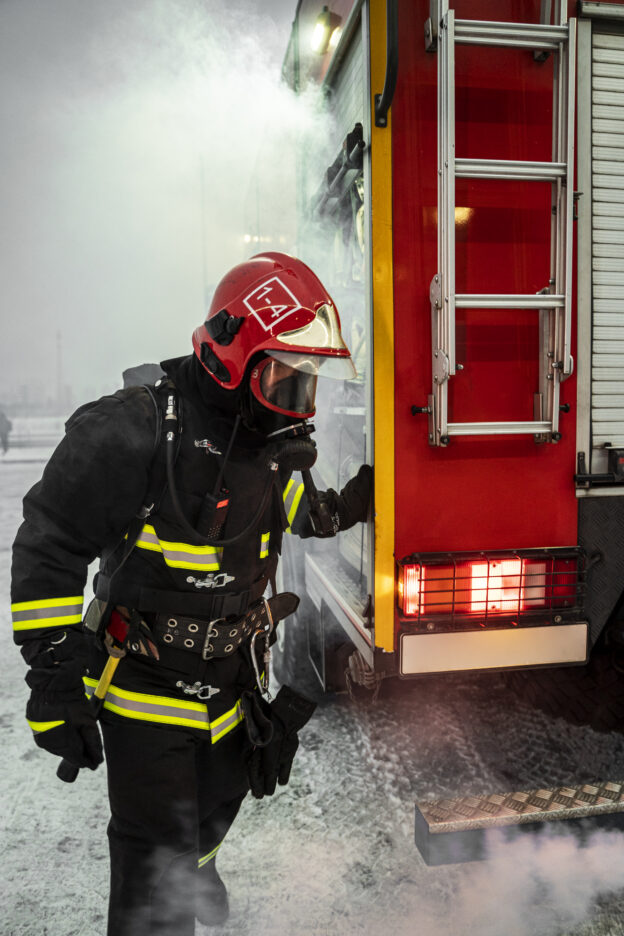
Do you have ever been burnt by fire? Because it is the most painful thing and the one who suffered from it can only describe the pain. Therefore, it is very important to respect heat and flame. Burns are among the most serious types of injuries. They don’t heal quickly and are excruciatingly painful. In some cases, keeping the wound clean while it heals can be a chore.
Often, the cause of burns is fire. Because of this, fire can be extremely dangerous in the right circumstances. Many businesses now have strict rules and regulations in place to reduce risks.
If you think fire problems at workplaces will not affect you, you are wrong. Because burn injuries are very common, particularly in the Oil and Gas industries, Iron Working, Welding, and others. In fact, according to the American Burn Association, approximately 486,000 people received medical treatment for burns in 2016. They can occur at any time, so it’s important to take some precautionary measures.
The fundamentals of putting out a fire (especially once you’re on fire) should have been covered in elementary school. Stop, Drop, and Roll are excellent suggestions for what to do if you’re already on fire. But can we do something to completely avoid it?
There is, as it turns out. Staying away from hot things is one of the most common ways to avoid burns. But that isn’t an option for certain occupations. For this reason, flame-retardant and flame-resistant clothes regulations became standardized for those industries. But what exactly are they? What’s the distinction? And how do they function? Is it better to be fire-resistant than fire-retardant? Or is it vice versa? Let us investigate.
What Is the Difference Between Flame-Resistant and Fire-Retardant?
People frequently misuse the terms “flame resistant” and “fire retardant”. While these two terms sound very similar, they are not entirely interchangeable. For the average person, this can be perplexing. We want you to know exactly what you need and which product is best for the job.
First and foremost, the terms “flame” and “fire” are interchangeable. You can use them interchangeably to describe the same concept. That, however, is not the issue. However, confusion arises when comparing “resistant” to “retardant.” They do not describe the same thing, unlike flame and fire. These terms can be deceptive. It’s always important to know which is which. Because if you’re supposed to use one but purchase the other, you could face serious consequences. It might burn you!
Flame-Resistant

This term refers to a material that is naturally resistant to catching fire. It is self-extinguishing. This means it does not melt or drip when exposed to high temperatures. Wool, for example, is widely regarded as the most flame-resistant natural fiber. This is due to the fact that it is difficult to ignite, and flames are frequently extinguished within the fibers.
So, flame-resistant clothes comprise materials that are inherently nonflammable. These materials’ chemical structures have flame resistance built in. Fabrics made from these materials help to prevent fire spread. When they are close to the fire, they will not melt or drip. This means the flame-resistant fabric has a natural ability to deter fire. But unfortunately, some flame-resistant clothes have mixed material, therefore they will burn. But only very slowly and frequently self-extinguish. So, when you go to buy flame-resistant clothes, be careful of the mixed material garment.
Listed Below Are Several Flame Resistant Materials:
- Coated Nylon
- Carbon Foam
- Wool
- Leather
- Gypsum Boards
- Concrete
- Cement
- Glass
Fire-Retardant
A retardant, on the other hand, is defined as a material that has been chemically treated to self-extinguish. Consider fabric drapes that will not melt or drip. The melting and dripping of a fabric is the most dangerous safety concern. Because the melted material can cause severe skin damage.
So, a flame retardant fabric is a chemically treated garment. So that, it burns slowly or self-extinguishes when exposed to an open flame. These fabrics can be made of any material, but to be flame retardant, they must be treated with special chemicals.
Because some fire retardant chemicals contain toxic chemicals, they are not as popular as they once were. To help reduce the spread of fire, professionals use these chemicals on plastics and furniture. Some of them have evolved to include additional benefits such as stain guarding.
Flame Retardant Sprays You Should Try:
- Master Flame – Fire Retardant
- TriNova Fabric Protector Spray and Stain Guard
- ForceField – FireGuard
- No-Burn Original Fire Retardant
- BanFire Spray-On Fire Retardant
Importance of Flame Retardant and Flame Resistant Clothing
Flame retardant and flame-resistant clothes are essential in a variety of industries. Fire retardant and resistant fabrics are critical factors for engineers in industries ranging from oil and gas to furniture manufacturing.
When it comes to safety equipment, this is no exception. Fire-resistant/retardant safety vests, shirts, and gloves are all examples of equipment. They provide users with an additional layer of flame protection. Flame retardant/resistant apparel is very safe, but avoid exposing it to heat for an extended period of time.
Flame Resistant Vs Flame Retardant – Which is better?
While both flame-resistant and flame-retardant methods have their applications in safety apparel and other industries, flame resistance is likely to be regarded as much safer than flame-retardant alternatives. There have been numerous discussions about the toxic chemicals found in flame retardants. They have a negative impact on our health and even the environment.
The best way to deal with fire is to avoid it whenever possible in dangerous situations. In fact, even in a safe environment, fire is dangerous and you must monitor it all the time. Flame-resistant and flame-retardant clothing keep you safe and prevent injury until you can move to a safe location. They do not allow you to stand in a fire.
Conclusion
Fire-resistant paints, varnishes, and clothing act as an insulator against fire. They protect a variety of substrates. They allow them to retain their integrity for a longer period of time. It also reduces the amount of time it takes for a fire to break through a treated surface.
Whereas, fire retardants work by reducing the combustibility of vulnerable substrates like wood and slowing the rate at which a fire spreads. They can also allow small fires to extinguish themselves and prevent many larger-scale fires.